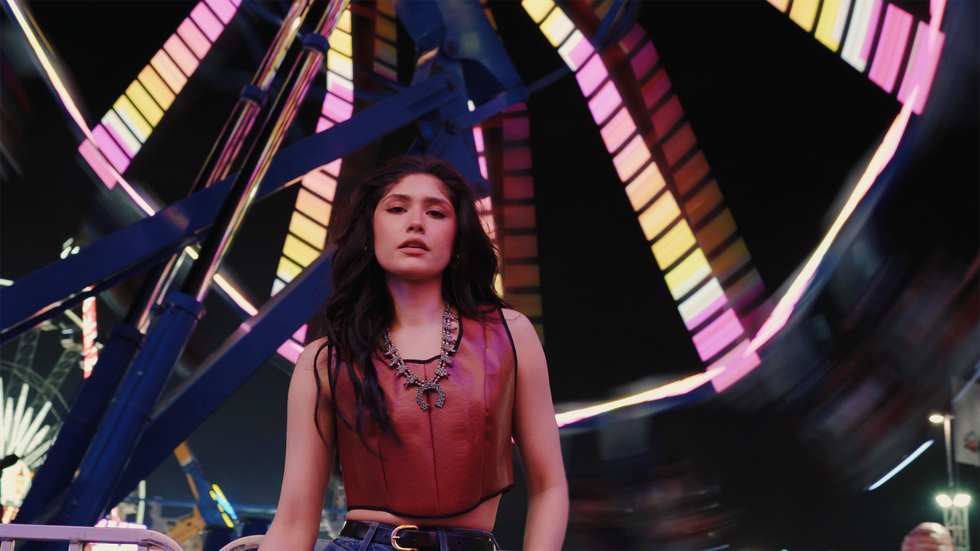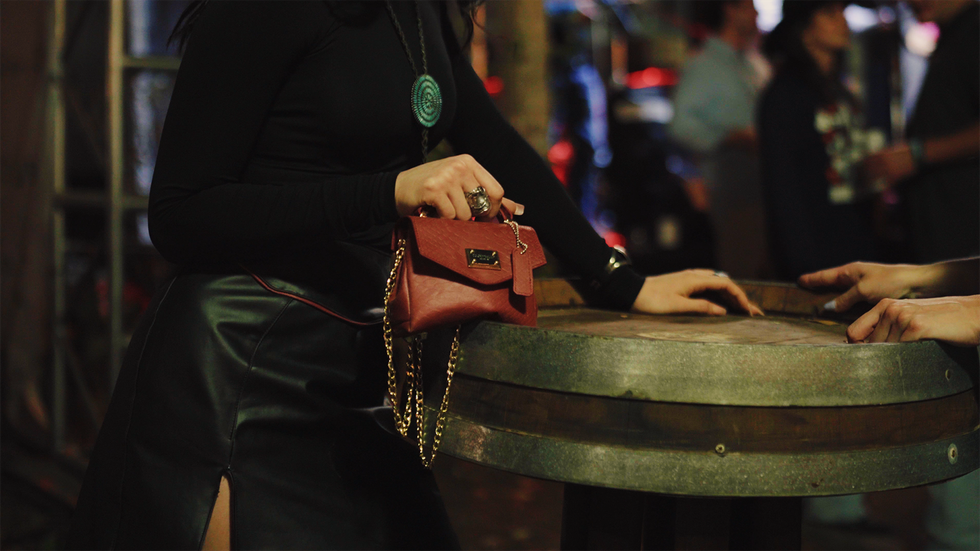sustainable materials
Houston startup unveils sustainable bio-based leather at the rodeo
Last month’s Houston Livestock Show and Rodeo stirred up another rootin’ tootin’ time for Houstonians and beyond.
But before the annual event galloped into the sunset, there were quite a few memorable innovations on display, with one notably coming from Rheom Materials.
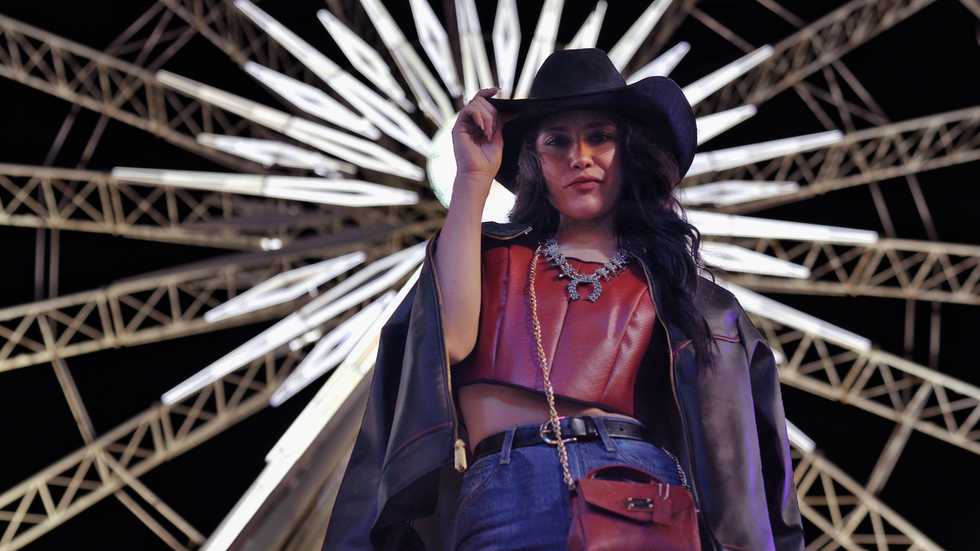
The Houston-based pioneer of next-generation materials presented its scalable, bio-based alternative known as Shorai, a 93 percent bio-based leather, through two custom, western-inspired outfits that showed off cowboy flair through a sustainable lens.
“I'm a Houstonian, I love the rodeo,” Megan Beck, Rheom’s business development manager, recalls. “We're sitting there talking about it one day and we're like, ‘Okay, we've got to do something with this leather to show people how good it can look in apparel, how easy it is to wear.’”
Buoyed by the idea that their materials are meant to “change your impact, not your life,” Rheom captured the real-life energy of their bio-leather outfits under the rodeo’s neon lights in a short commercial video and photo shoot with models donning the samples, while dancing and enjoying the festivities. Rheom created a skirt, a leather jacket, and then a leather top for the look.
“Houston is such a vibrant city,” Beck says. “There's so much innovation here. I think the rodeo is just a really, really great example of that. And so we wanted to take this opportunity to take some of these garments out there and go on the slide, go on some of the rides, go into the wine garden and go dancing, because if you've ever felt some of the materials in the market in this space, they're very stiff, you can't really move in them, they're a little fragile, they kind of fall apart.”
Not only do the models in the video look fashionable, but they also look comfortable, and the leather looks natural and supple. And to the naked eye, Shorai appears to be like the leather most wearers are accustomed to.
“What we really wanted to showcase in this is the energy and the movement of the leather, and to show people how good it can look in apparel, and how easy it is to wear, which I think we were able to accomplish,” Beck says.
Next up, Beck says Rheom wants to scale production of Shorai, the Japanese word for “future,” at a competitive price point, while also reducing its carbon footprint by 80 percent when compared to synthetic leather. According to Beck, Rheom plans to see Shorai products come to market sometime this year.
“We have companies globally right now that are testing materials, that are prototyping, that are making garments, making handbags and footwear, and making eyewear because we have a plastic, as well,” Beck says. “So, this year, I do believe we'll start seeing those products actually come to market, which is very, very exciting for us.”
And with their large-scale production partner already set up for Shorai, Rheom plans to start its first production run of the product soon.
“In April, we'll actually be starting our first production run,” Beck says. “We'll be doing it at full scale, full width, and a full run of materials. So over the next five years, we're only going to just try to increase that capacity.”
----
This story originally appeared on our sister site, InnovationMap.