step by step
CenterPoint’s Greater Houston Resiliency Initiative makes advancements on progress
CenterPoint Energy has released the first of its public progress updates on the actions being taken throughout the Greater Houston 12-county area, which is part of Phase Two of its Greater Houston Resiliency Initiative.
The GHRI Phase Two will lead to more than 125 million fewer outage minutes annually, according to CenterPoint.
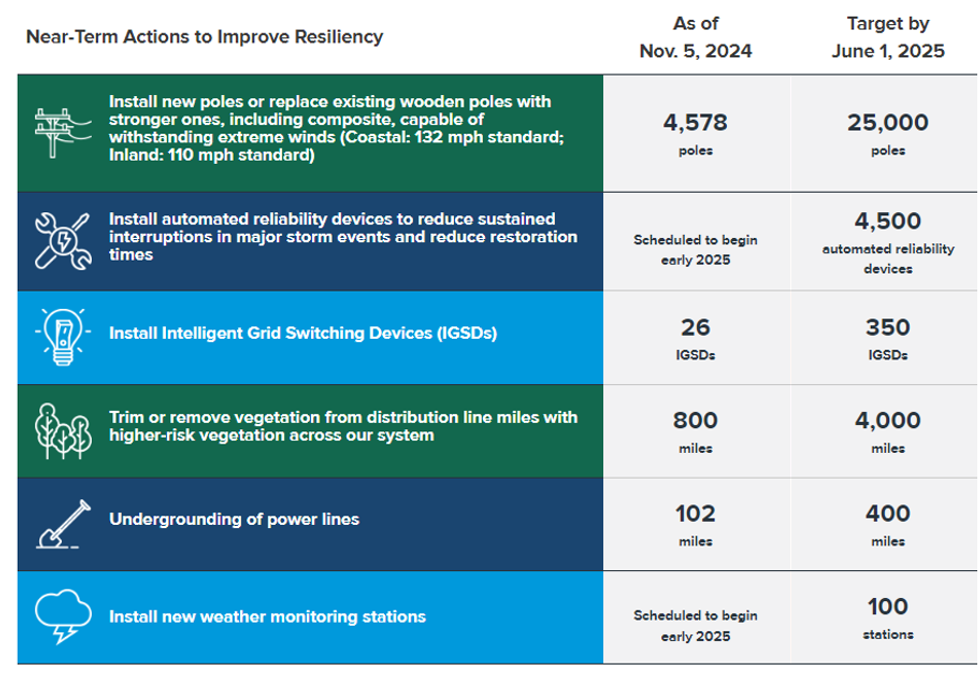
According to CenterPoint, they have installed around 4,600 storm-resilient poles, installed more than 100 miles of power lines underground, cleared more than 800 miles of hazardous vegetation to improve reliability, and installed more self-healing automation all during the first two months of the program in preparation for the 2025 hurricane season.
"This summer, we accomplished a significant level of increased system hardening in the first phase of the Greater Houston Resilience Initiative,” Darin Carroll, senior vice president of CenterPoint Energy's Electric Business, says in a news release.
”Since then, as we have been fully engaged in delivering the additional set of actions in our second phase of GHRI, we continue to make significant progress as we work toward our ultimate goal of becoming the most resilient coastal grid in the country,” he continues.
The GHRI is a series of actions to “ strengthen resilience, enable a self-healing grid and reduce the duration and impact of power outages” according to a news release. The following progress through early November include:
The second phase of GHRI will run through May 31, 2025. During this time, CenterPoint teams will be installing 4,500 automated reliability devices to minimize sustained interruptions during major storms, reduce restoration times, and establish a network of 100 new weather monitoring stations. CenterPoint plans to complete each of these actions before the start of the next hurricane season.
“Now, and in the months to come, we will remain laser-focused on completing these critical resiliency actions and building the more reliable and more resilient energy system our customers expect and deserve," Carroll adds.
CenterPoint also announced that it has completed all 42 of the critical actions the company committed to taking in the aftermath of Hurricane Beryl. Some of the actions were trimming or removing higher-risk vegetation from more than 2,000 power line miles, installing more than 1,100 more storm-resilient poles, installing over 300 automated devices to reduce sustained outages, launching a new, cloud-based outage tracker, improving CenterPoint's Power Alert Service, hosting listening sessions across the service area and using feedback.
In October, CenterPoint Energy announced an agreement with Artificial Intelligence-powered infrastructure modeling platform Neara for engineering-grade simulations and analytics, and to deploy Neara’s AI capabilities across CenterPoint’s Greater Houston service area.