California co. announces fully sustainable, hydrogen-powered data center in Houston
moving in
The Houston area will soon be home to what's being lauded as the first fully sustainable 1-gigawatt data center on a 600-acres site east of Houston.
Data center-as-a-service company ECL, headquartered in Mountain View, California, announced its plans to build the ECL TerraSite-TX1. Hardware and cloud service company Lambda will serve as its first tenant. Lambda and other AI leaders will get access to necessary space and power for the next wave zero emission innovations.
Phase 1 of TerraSite-TX1 will be complete by summer of 2025 with a cost of approximately $450 million. The 50 megawatt of data center capacity will be utilized by data center cloud and AI cloud operators. The 1-gigawatt site will be constructed at a cost of approximately $8 billion. The funding will come from ECL and financial partners.
ECL Terrasite-TX1 comes at a needed time for Texas with The Electric Reliability Council of Texas stating on June 12 that the state’s power grid needs will grow approximately double by 2030. This is due in part to the growth of data centers and AI. The ECL Terrasite-TX1 is built to help eliminate the stress on the state’s power grid and help facilitate “state-level economic development and growth of the AI industry,” according to a news release.
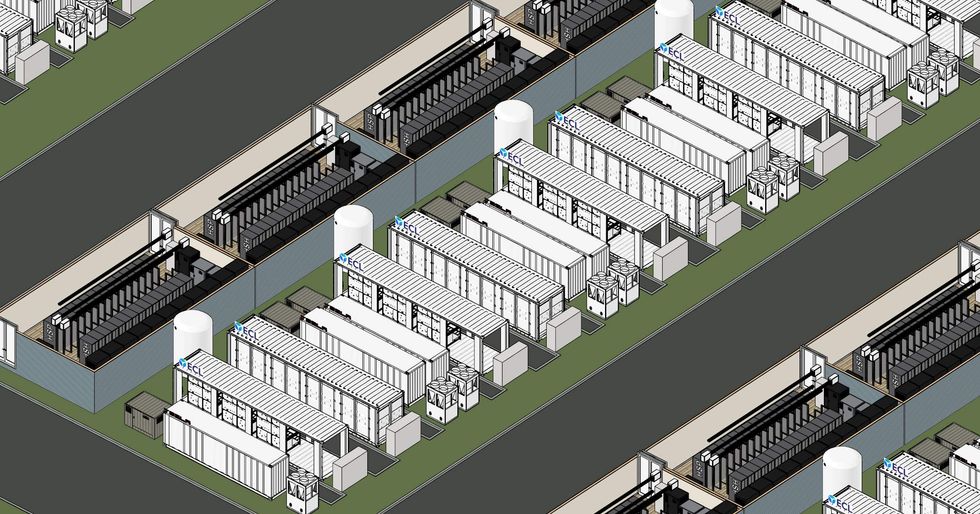
ECL data centers are built to be modular, which allows for expansion in 1-megawatt increments. They are “ built to suit” and delivered in less than 12 months, which is shorter than the industry standard of 36 to 48.
“While others talk about delivering off-grid, hydrogen-powered data centers in five, ten, or 20 years, only ECL is giving the AI industry the space, power, and peace of mind they and their customers need, now,” Yuval Bachar, co-founder and CEO of ECL, says in a news release. “The level of innovation that we have introduced to the market is unprecedented and will serve not only us and our customers but the entire data center industry for decades to come.”
ECL’s ECL-MV1 is the world’s first off-grid, hydrogen-powered modular data center that operates 24/7 with zero emissions, less noise, and a negative water footprint that replenishes water to the community. ECL-MV1 offers a 10x increase in “energy efficiency with a power usage effectiveness of 1.05 and a 7-times improvement in data density per rack, which is ideal for AI high-density demand” according to the release.
“The data center technology committed to by ECL is truly transformative in the industry,” Lambda's Vice President for Data Center Infrastructure Ken Patchett adds. “We believe ECL’s technology could unlock a powerful and eco-conscious foundation for AI advancement. This new infrastructure could give researchers and developers essential computational resources while drastically reducing the environmental impact of AI operations.”
- ExxonMobil’s low-carbon hydrogen project in Baytown adds Air Liquide as partner ›
- Chesapeake Energy backs Houston geothermal tech co. in $17M series A ›
- Houston geothermal energy startup grows local office presence ›
- Houston-area company specializing in creating clean campuses announces new data center project ›
- Google to invest $1B in clean energy, data center tech in Texas ›
- Houston tech hub secures $40M to meet rising data center needs ›
- New collaboration to build data center microgrid in Houston ›






 Acquisitions and agreements fuel the top Houston energy news to knowCatch up on our top news for the first half of February. Courtesy photo
Acquisitions and agreements fuel the top Houston energy news to knowCatch up on our top news for the first half of February. Courtesy photo


