big win
Rice University team breaks records with new sunlight-to-hydrogen device
A team of Rice University engineers have developed a scalable photoelectrochemical cell that converts sunlight into clean hydrogen at a record-setting pace.
The lab led by Aditya Mohite, an associate professor at Rice, published the findings in a study in Nature Communications late last month, in collaboration with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, which is backed by the Department of Energy. In it, the team details how they created a device that absorbs light, converts it into electricity, and then uses the electricity to split water molecules and generate hydrogen.
Austin Fehr, a chemical and biomolecular engineering doctoral student at Rice and one of the study’s lead authors, says in a statement that the device "could open up the hydrogen economy and change the way humans make things from fossil fuel to solar fuel."
The device has a high solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency rate of 20.8 percent, which has yet to be reached with this type of technology, according to a release from Rice. In addition to its speed, this device is groundbreaking because it uses low-cost metal-halide perovskite semiconductors to power the reaction.
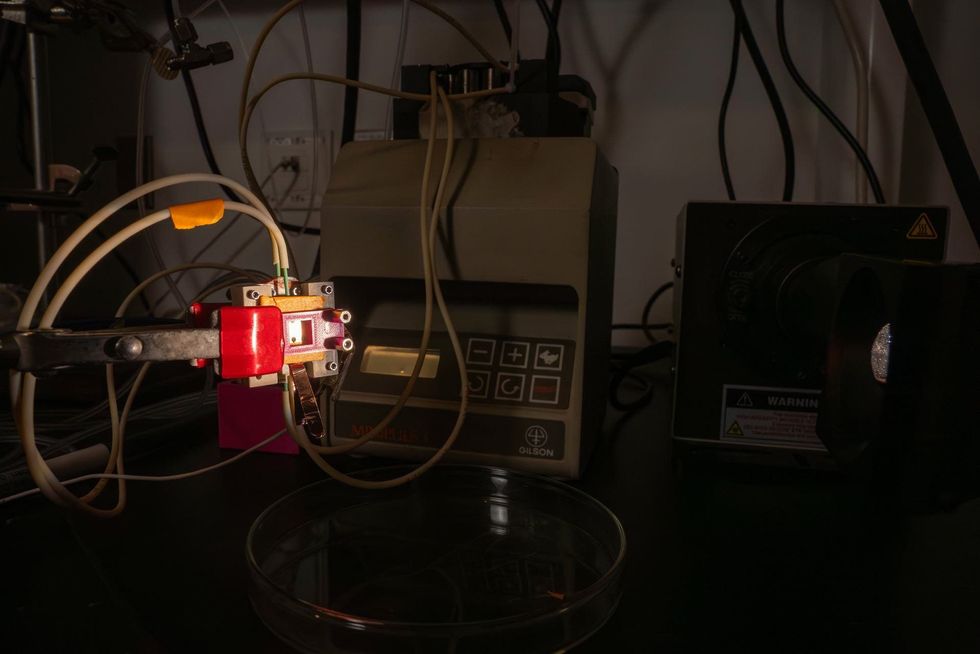
“Using sunlight as an energy source to manufacture chemicals is one of the largest hurdles to a clean energy economy,” Fehr says in the statement. “Our goal is to build economically feasible platforms that can generate solar-derived fuels. Here, we designed a system that absorbs light and completes electrochemical water-splitting chemistry on its surface.”
To create the device the Mohite lab turned their existing solar cell into a reactor to split water into oxygen and hydrogen. However they continued running into issues with the semiconductors being "extremely unstable in water," according to Rice.
After two years of trials and errors, the team uncovered that by adding two layers of barriers to the semiconductors they were able to reach these record-breaking efficiency rates.
The team has also shown uses for their double barrier design with different semiconductors and for different reactions.
“We hope that such systems will serve as a platform for driving a wide range of electrons to fuel-forming reactions using abundant feedstocks with only sunlight as the energy input,” Mohite says in the statement.
The device joins another game-changing product shared in a Rice research study in recent weeks. Last month, a Rice University lab led by Haotian Wang, the William Marsh Rice Trustee Chair and an associate professor at Rice, shared their findings on how their simple plug-and-play device removes carbon dioxide from air capture to induce a water-and-oxygen-based electrochemical reaction.
Rice also recently opened registration for its 20th anniversary of Energy Tech Venture Day. Click here to register for the event on Sept. 21.





