Houston lab's breakthrough light-harvesting processes near market readiness
coming soon
A groundbreaking Rice University lab has made further strides in its work to make harvesting light energy more efficient and stable.
Presented on the cover of a June issue of Science, a study from Rice engineer Aditya Mohite's lab uncovered a method to synthesize a high-efficiency perovskite solar cell, known as formamidinium lead iodide (FAPbI3), converting them into ultrastable high-quality photovoltaic films, according to a statement from Rice. Photovoltaic films convert sunlight into electricity.
The new process makes solar cells that are about 10 times more durable than traditional methods.
“Right now, we think that this is state of the art in terms of stability,” Mohite said in a statement. “Perovskite solar cells have the potential to revolutionize energy production, but achieving long-duration stability has been a significant challenge.”
The change come from "seasoning" the FAPbI3 with 2D halide perovskites crystals, which the Mohite lab also developed a breakthrough synthesis process for last year
The 2D perovskites helped make the FAPbI3 films more stable. The study showed that films with 2D perovskites deteriorated after two days of generating electricity, while those with 2D perovskites had not started to degrade after 20 days.
“FAPbI3 films templated with 2D crystals were higher quality, showing less internal disorder and exhibiting a stronger response to illumination, which translated as higher efficiency," Isaac Metcalf, a Rice materials science and nanoengineering graduate student and a lead author on the study, said in the statement.
Additionally, researchers say their findings could make developing light-harvesting technologies cheaper, and can also allow light-harvesting panels to be lighter weight and more flexible.
"Perovskites are soluble in solution, so you can take an ink of a perovskite precursor and spread it across a piece of glass, then heat it up and you have the absorber layer for a solar cell,” Metcalf said. “Since you don’t need very high temperatures ⎯ perovskite films can be processed at temperatures below 150 Celsius (302 Fahrenheit) ⎯ in theory that also means perovskite solar panels can be made on plastic or even flexible substrates, which could further reduce costs.”
Mohite adds this has major implications for the energy transition at large.
“If solar electricity doesn’t happen, none of the other processes that rely on green electrons from the grid, such as thermochemical or electrochemical processes for chemical manufacturing, will happen,” Mohite said. “Photovoltaics are absolutely critical.”
The Mohite lab's process for creating 2D perovskites of the ideal thickness and purity was published in Nature Synthesis last fall. At the time, Mohite said the crystals "hold the key to achieving commercially relevant stability for solar cells."
About a year ago, the lab also published its work on developing a scalable photoelectrochemical cell. The research broke records for its solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency rate.- Things to know this week: Houstonian's guide to CERAWeek 2024 ›
- Woodside Energy backs $12.5M clean energy accelerator for new technologies ›
- Rice University team breaks records with new sunlight-to-hydrogen device ›
- Houston software company equips green project developers with IRA compliance tools - Energy Capital ›






 Rice University announced the new climate tech initiative backed by Woodside Energy this week. Photo by Natalie Harms/InnovationMap
Rice University announced the new climate tech initiative backed by Woodside Energy this week. Photo by Natalie Harms/InnovationMap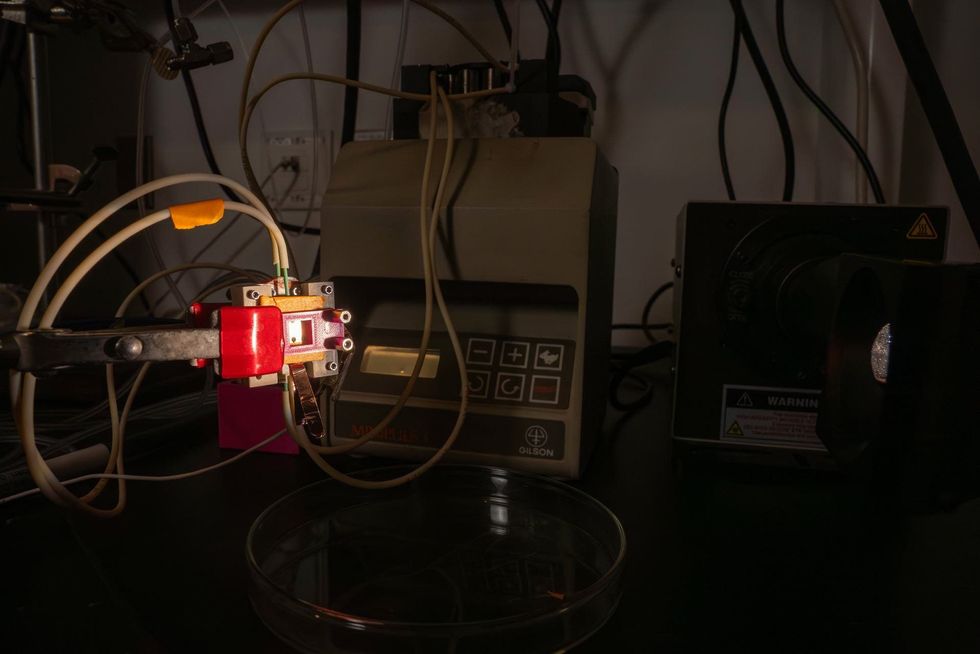 A photoreactor developed by Rice University’s Mohite research group and collaborators achieved a 20.8 percent solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency. Photo courtesy Gustavo Raskoksy/Rice University
A photoreactor developed by Rice University’s Mohite research group and collaborators achieved a 20.8 percent solar-to-hydrogen conversion efficiency. Photo courtesy Gustavo Raskoksy/Rice University