Houston-based Talos Energy Inc. announced its transition plans for it's top executive position.
Tim Duncan stepped down from his role as president and CEO, the company announced last week. Duncan, who held the position since 2012, will be replaced by board member, Joseph A. Mills, who will serve as interim president and CEO as the Talos board of directors searches for a successor.
"On behalf of the Board and the entire Talos team, I want to express our gratitude to Tim for his invaluable contributions to the Company," Neal P. Goldman, chairman of Talos' Board of Directors, says in a news release. "We have complete confidence in Joe's capabilities to carry out Talos' strategy as we search for a new CEO to lead Talos into the future and unlock further value. Mills brings a wealth of industry experience and knowledge, boasting over 42 years in senior leadership positions and serving on the boards of both public and private companies in the oil and gas sector."
Mills, CEO of Samson Resources II since March 2017, joined Talos as a board member in March. He has 42 years of experience in oil in gas.
"I'm honored to step in as interim CEO of Talos," Mills adds. "The Board has played an active role guiding and evaluating our strategic approach, and I am confident about Talos's direction and strategy. Our commitment remains firm in delivering compelling value for our shareholders. I look forward to working closely with the Board and leadership team, drawing on their extensive knowledge to advance our strategic priorities during this transitional period."
Talos Energy is an upstream exploration and production business operating in the United States Gulf of Mexico and offshore Mexico. Talos is a part owner of the Bayou Bend CCS LLC joint venture, a carbon capture and storage project. Earlier this year, Talos made a $1.29 billion acquisition to expand deepwater assets.
- 3 things to know this week: Meet Chevron's UH fellows, Bayou Bend CCS's newest partner, can't-miss events ›
- Houston companies land DOE vouchers for clean tech ›
- Equinor buys into massive CCS joint venture project near Houston ›
- Talos makes $1.3B acquisition, Sunnova's new tech partner, and more trending Houston news ›
- Talos Energy sells off low carbon arm to TotalEnergies in $148M deal ›






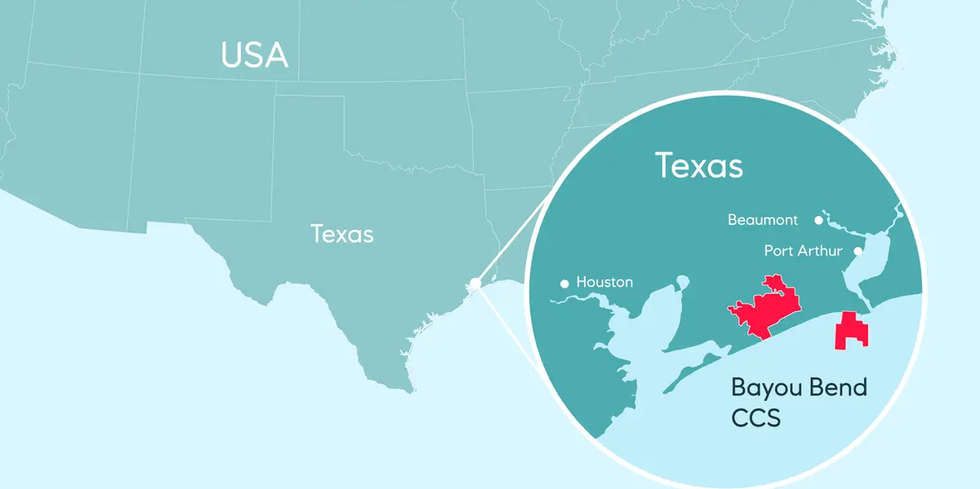 The project is located in southeast Texas, about 70 miles outside of Houston. Image via equinor.com
The project is located in southeast Texas, about 70 miles outside of Houston. Image via equinor.com