Houston energy innovators create more efficient logistics platform for industry
now loading
In a world where ”the customer is always right," two Houston founders have followed that rule right to their next venture.
Breaker19 — a groundbreaking mobile application built in late 2023 to be an efficient oilfield trucking and hotshot marketplace — was co-founded by Rodney Giles and Tyler Cherry. The native Houstonians also co-founded BidOut, a leading Oil & Gas procurement platform in 2021.
“About a year ago, one of our BidOut clients, a large operator, came to us and basically said that the biggest problem they have in the oil field is ordering trucks,” remembers Giles. “From there, they asked would we be willing to build something similar to Uber, but for oilfield logistics and trucking? So, we built Breaker19.”
After their customer presented a challenge, Giles and Cherry got to work. They envisioned the technical architecture almost immediately and assembled a team of software engineers to build an in-house application in less than a year.
“We launched Breaker19 in November 2023, and my goodness, it has taken off like crazy,” says Giles. “It is growing incredibly fast. We’re doing hundreds of truckloads a day now, all throughout West Texas, South Texas, North Dakota, really all over the U.S.”
Now, armed with such large publicly traded companies as British Petroleum, Breakout19 has a network of more than 1,500 trucks similar to transportation companies like Uber, where drivers make themselves available to be dispatched according to their health, safety and environmental requirements.
Breaker19 is doing so well, in fact, that it’s sped past Giles and Cherry’s original collaboration, BidOut.
“Breaker 19's probably, you know, growing ten times of where BidOut even was in its early days,” says Giles. “So, we'll always explore options that make sense for our shareholders. Fortunately, my co-founder and I have previous companies that we built and sold and have experience in scaling and have experiences in multiple departments, whether it be finance or sales or marketing or operations.
“So, currently, we do operate BidOut and Breaker19 separately, but they are, you know, through common operating structures. And, you know, we're able to maintain the scale and maintain the growth right now. And right now, the company is doing great financially and has cash flow positives. So, for us, you know, our goal is just to continue. I feel like we've kind of solved an archaic problem and did it in a really simple way, and it's working out pretty well.”
And it all started with a simple question from a customer — "Hey, can you guys come up with something like this?"
“It all came together just by listening to our customer’s needs,” says Giles. “And we always try to go into our clients and help them with a lot of what they do. But we always want to know about what their other pain points are. You know, there's still people, you know, that are operating with very archaic processes, very, you know, manual back-office processes. And our job is to speed them up with software. And so Breaker19 was able to do that.”
Practically speaking, Breaker19 is more than a software solution. It also closes the gap between qualified drivers and end clients by vetting participants for the platform in an efficient and pragmatic fashion.
“We have a very rigorous vetting process for the drivers,” Giles explains. “I mean, that's really what makes the oil and gas trucking industry so unique. Insurance requirements have to be significantly higher than most carriers. They have to go through very well-funded safety trainings where they are familiar with the oil field. And then number three, these drivers have to have personal protective equipment. They have to have flame-retardant clothing, they have to have slo-mo boots and they have to have hard hats.”
Procedure is important, but professionalism is equally important to Breaker19.
“You know, we do not allow the carrier to show up on a customer's locations in shorts and flip-flops or Crocs and, you know, be protected,” says Giles. “And so, for what we're dealing with is very mission critical, but also very, you know, very high-risk.
“For example, we are checking insurance statuses four times a day. If a carrier were to cancel their insurance, we're aware of it immediately because we want to make sure that we always have active insurance in place. So, we have a process that these carriers go through. Again, we've got over 1,500 of them now that are well-vetted and well-qualified.”
As Breaker19 continues to scale, Giles and Cherry hope their burgeoning app becomes the go-to ordering platform for the entire oil and gas industry for all of their trucking, hot shot and transportation needs.
“We're bringing on some significant, large enterprise clients right now that make up 10% of the U.S. market share for each customer,” says Giles “So I think when we start to compound those, I think we easily see the trajectory there as really being something that's taking off pretty fast. So, I think at the end of the day, we just hope to keep delivering a great experience for our clients, make their ordering process easy.”
With both BidOut and Breaker19 doing great financially, proud Klein Oak High School alums Giles and Cherry have purchased a steer to support Texas youth and agricultural causes. Additionally, moving forward, the duo pledges to give away a full steer each month to a customer of their Breaker19 platform.
"We are passionate about giving back to our community and nurturing the next generation of leaders in Texas," says Cherry. "Having personally experienced the transformative impact of FFA, we saw this initiative as a meaningful way to both support local agriculture and provide our clients with a taste of authentic Texas beef.”
———
This article originally ran on InnovationMap.






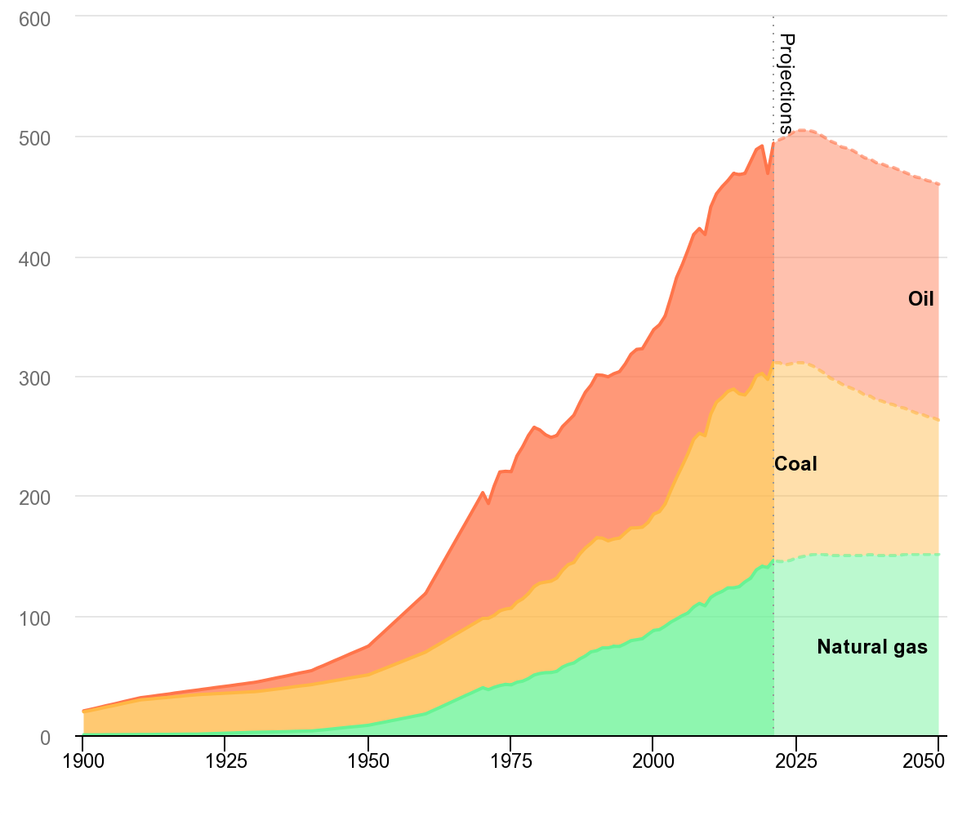 Demand for natural gas and oil are expected to level out, as demand for coal shrinks to meet goals for lower carbon emissions. Photo courtesy of IEA, license CC by 4.0Demand for natural gas and oil are expected to level out, as demand for coal shrinks to meet goals for lower carbon emissions. Photo courtesy of IEA, license CC by 4.0
Demand for natural gas and oil are expected to level out, as demand for coal shrinks to meet goals for lower carbon emissions. Photo courtesy of IEA, license CC by 4.0Demand for natural gas and oil are expected to level out, as demand for coal shrinks to meet goals for lower carbon emissions. Photo courtesy of IEA, license CC by 4.0