Automation company signs on to power up $10 billion hydrogen project in South Texas
seeing green
Electrification and automation company ABB, whose U.S. headquarters for its Energy Industries business is in Houston, has tentatively agreed to supply power for a $10 billion hydrogen project in South Texas.
Under a new memorandum of understanding, ABB plans to collaborate with Houston-based Green Hydrogen International on the Hydrogen City project. The first phase of the project is expected to generate 280,000 tons of green hydrogen per year. This green hydrogen will then be converted to one million tons of green ammonia each year.
“Together, we will enable efforts to decarbonize global industry and progress towards a net-zero future,” Brandon Spencer, president of ABB Energy Industries, says in a news release.
The memorandum of understanding calls for ABB’s technology to be assessed for delivery of solar and onshore wind energy to the 2.2-gigawatt electrolyzer facility at Hydrogen City.
The project will store up to 24,000 tons of green hydrogen in underground salt caverns. A 75-mile pipeline to the nearby Corpus Christi energy port will carry the green hydrogen to an ammonia production facility. At this facility, green hydrogen will be turned into green ammonia that’ll be shipped to Europe and Asia.
Green Hydrogen International is in talks with companies interested in using green hydrogen from Hydrogen City as feedstock for sustainable aviation fuel and e-methane.
Hydrogen City will serve a global green ammonia market whose value is projected to reach $17.9 billion by 2030. Construction on Hydrogen City is scheduled to start in 2026, with initial production set for 2030.
Green Hydrogen International unveiled the multiphase Hydrogen City project in 2022, saying it would be “the world’s largest green hydrogen production and storage hub.” At his month’s CERAWeek in Houston, officials provided an update on Hydrogen City.
“Ammonia has the potential to support decarbonization efforts as part of the energy transition through its use as an alternative fuel for heavy transport such as shipping, as well as its current major use in fertilizer production,” ABB says in the news release.
Last October, Green Hydrogen International announced a Hydrogen City partnership with Japanese oil and gas giant Inpex, whose U.S. outpost is in Houston.






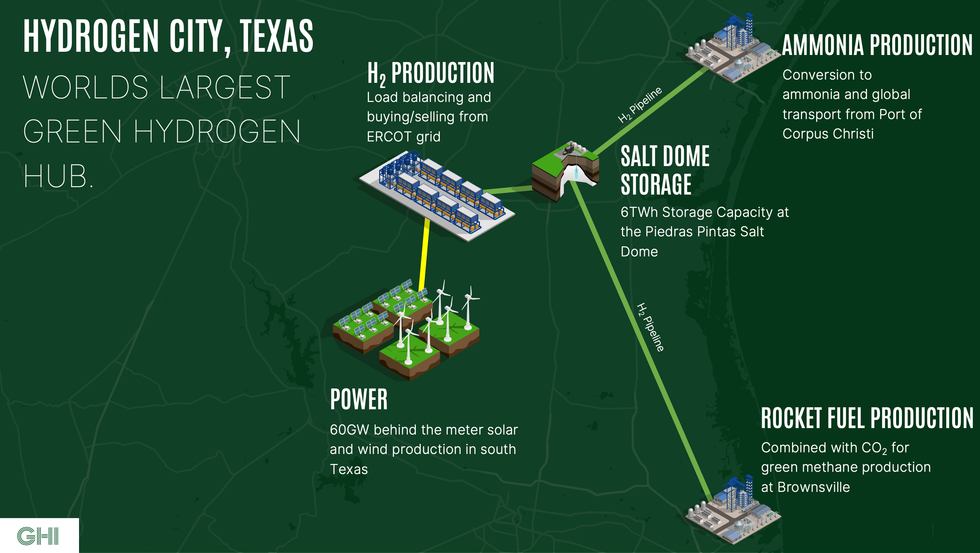 Image via ghi-corp.com
Image via ghi-corp.com



