New UH white paper pushes for national plastics recycling policy
plastics paper
The latest white paper from the University of Houston’s Energy Transition Institute analyzes how the U.S. currently handles plastics recycling and advocates for a national, policy-driven approach.
Ramanan Krishnamoorti, vice president for energy and innovation at UH; Debalina Sengupta, assistant vice president and chief operating officer at the Energy Transition Institute; and UH researcher Aparajita Datta authored the paper titled “Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) for Plastics Packaging: Gaps, Challenges and Opportunities for Policies in the United States.” In the paper, the scientists argue that the current mix of state laws and limited recycling infrastructure are holding back progress at the national level.
EPR policies assign responsibility for the end-of-life management of plastic packaging to producers or companies, instead of taxpayers, to incentivize better product design and reduce waste.
“My hope is this research will inform government agencies on what policies could be implemented that would improve how we approach repurposing plastics in the U.S.,” Krishnamoorti said in a news release. “Not only will this information identify policies that help reduce waste, but they could also prove to be a boon to the circular economy as they can identify economically beneficial pathways to recycle materials.”
The paper notes outdated recycling infrastructure and older technology as roadblocks.
Currently, only seven states have passed EPR laws for plastic packaging. Ten others are looking to pass similar measures, but each looks different, according to UH. Additionally, each state also has its own reporting system, which leads to incompatible datasets. Developing national EPR policies or consistent nationwide standards could lead to cleaner and more efficient processes, the report says.
The researchers also believe that investing in sorting, processing facilities, workforce training and artificial intelligence could alleviate issues for businesses—and particularly small businesses, which often lack the resources to manage complex reporting systems. Digital infrastructure techniques and moving away from manual data collection could also help.
Public education on recycling would also be “imperative” to the success of new policies, the report adds.
“Experts repeatedly underscored that public education and awareness about EPR, including among policymakers, are dismal,” the report reads. “Infrastructural limitations, barriers to access and the prevailing belief that curbside recycling is ineffective in the U.S. contribute to public dissatisfaction, misinformation and, in some cases, opposition toward the use of taxpayers’ and ratepayers’ contributions for EPR.”
For more information, read the full paper here.
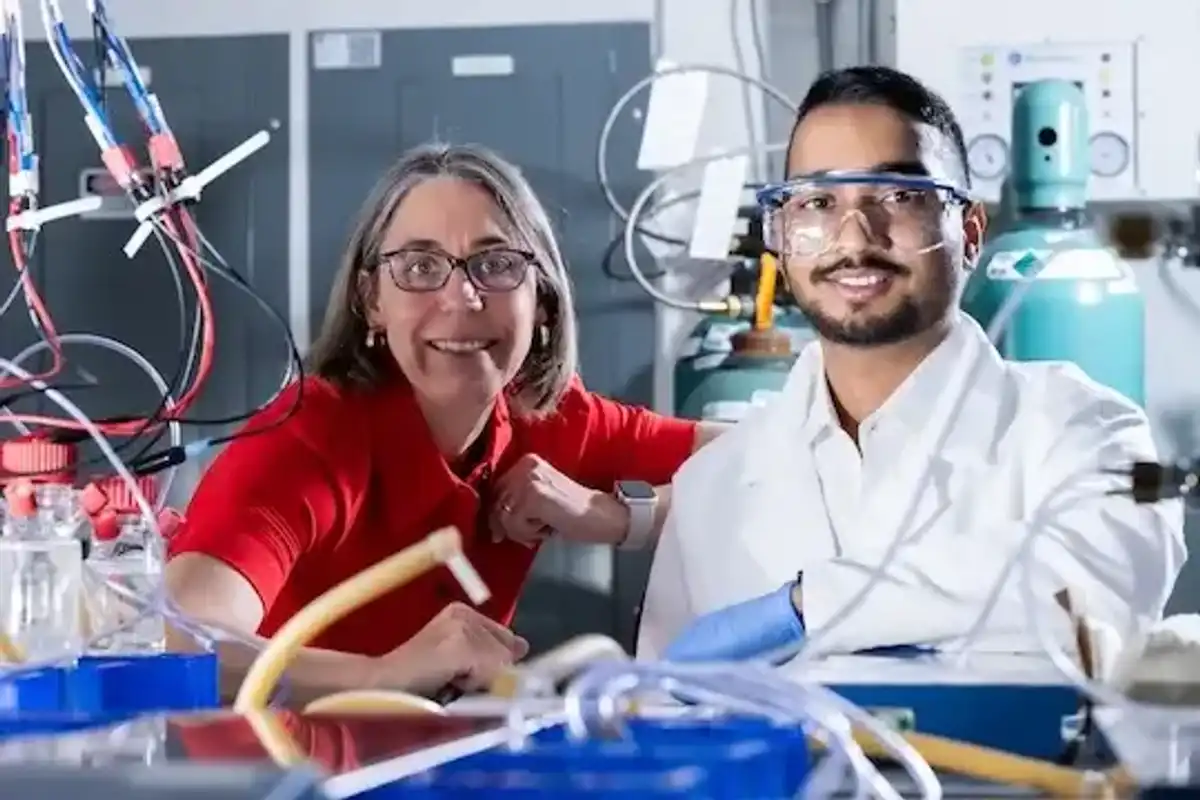











 Houston researchers make headway on developing low-cost sodium-ion batteries
Houston researchers make headway on developing low-cost sodium-ion batteries