A Norwegian energy company with its United States headquarters in Houston has announced it has acquired a significant chunk of a carbon capture and storage joint venture.
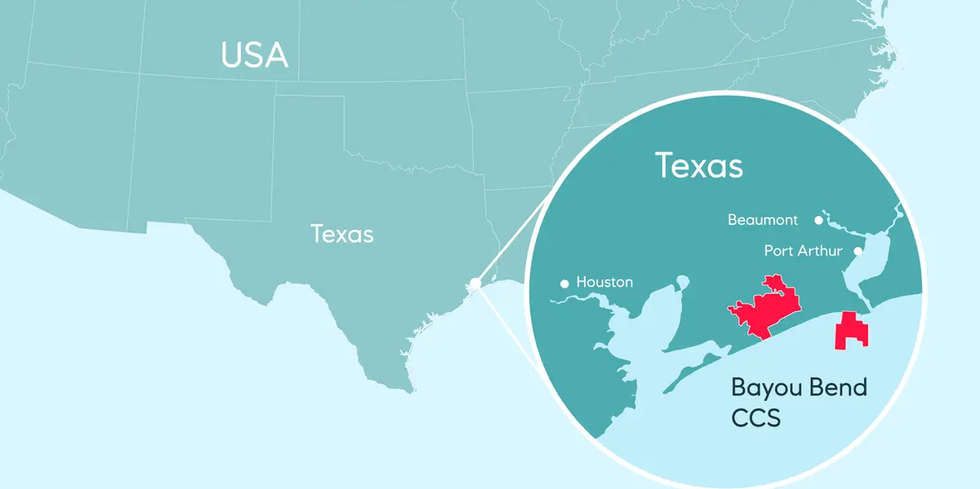
Equinor now owns a 25 percent interest in Bayou Bend CCS LLC, which is reported to be one of the largest domestic carbon capture and storage projects. The project — a JV between Chevron, Talos Energy Inc., and now Equinor, is located along the Gulf Coast in southeast Texas. The terms of the deal were not disclosed.
“Commercial CCS solutions are critical for hard-to-abate industries to meet their climate ambitions while maintaining their activity," Grete Tveit, senior vice president for Low Carbon Solutions in Equinor, says in a news release. "Entering Bayou Bend strengthens our low carbon solutions portfolio and supports our ambition to mature and develop 15-30 million tonnes of equity CO2 transport and storage capacity per year by 2035. Our experience from developing carbon storage projects can help advance decarbonization efforts in one of the largest industrial corridors in the US."
According to Equinor, it purchased its share through the acquisition of Carbonvert's subsidiary, Texas Carbon 1 LLC. Chevron, the operator, holds 50 percent interest, and Talos holds the other 25 percent interest.
“We look forward to working together with our partners to further mature this exciting project. Bayou Bend is Equinor’s first announced low carbon solutions project on the Gulf Coast. Alongside our upstream production and offshore wind developments, we’re strengthening our position as a broad energy company and expanding our footprint in the Gulf region,” Chris Golden, senior vice president and US Country Manager, says in the release. "Bayou Bend is a significant milestone towards growing our low carbon portfolio in the US.”
With about 140,000 gross acres of pore space for permanent CO2 sequestration and over one billion metric tons of gross potential storage resources, according to the release, Bayou Bend is positioned to be one of the largest CCS solutions in the US for industrial emitters.The project spans around 100,000 gross acres across Chambers and Jefferson Counties in southeast Texas, and approximately 40,000 gross acres offshore Beaumont and Port Arthur.
“Delivering lower carbon solutions to harder-to-abate industries is fundamental to Chevron New Energies’ mission, and as a Southeast Texas native, I know how vital these industries are to our local communities and their economies,” Chris Powers, vice president of CCUS at Chevron New Energies, in the release. “We thank Carbonvert for its work on the project, and we look forward to Equinor bringing its expertise and resources to Bayou Bend as it joins the partnership.”
Each of the company's low-carbon innovation arms — Low Carbon Solutions at Equinor, Chevron New Energies division, and Talos Low Carbon Solutions division — are collaborating on the project.
“We continue to make significant progress in developing Bayou Bend, which we believe will be a premier regional carbon storage hub solution for Texas’ largest industrial region. Equinor is a welcomed addition to the partnership. Their experience and track record further enhance the joint venture, which is committed to developing safe, reliable, cost-effective lower carbon solutions while enabling continued economic growth,” said Robin Fielder, executive vice president – Low Carbon Strategy and Chief Sustainability Officer of Talos.
In 2021, Texas General Land Office in Jefferson County, Texas, selected Talos and Carbonvert for the carbon storage lease, located in state waters offshore Beaumont and Port Arthur, Texas. Chevron joined the JV in May 2022. The project expanded earlier this year.